Machine Learning (ML) vs Artificial Intelligence (AI): crucial differences
Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) have received a lot of public interest in recent years, and both terms are practically commonplace in IT parlance. Despite their similarities, there are some important differences between ML and AI that are often neglected.
Therefore, we will cover the key differences between ML and AI in this blog so that you can understand how these two technologies vary and how they can be used together.
Let’s get started!
Understanding Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning (ML) is a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI) that automates the analysis and prediction of data using algorithms and statistical models. It allows systems to recognize patterns and correlations in large amounts of data and can be applied to a variety of applications such as image recognition, natural language processing, and others.
ML is fundamentally about learning from data. It is a continuous method of developing algorithms that can learn from past data and predict future data. In this approach, ML algorithms can continually improve their performance over time by discovering previously unknown or undetectable patterns.
Types of Machine Learning Algorithms
There are commonly 4 types of machine learning algorithms. Let’s get to know each one of them.
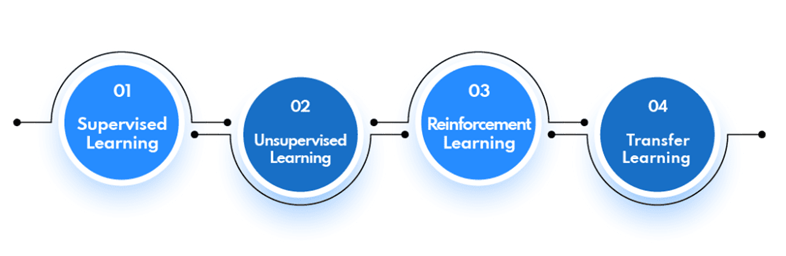
1. Supervised learning
Supervised learning includes providing the ML system with labeled data, which helps it understand how unique variables connect to each other. When presented with new data points, the system applies this knowledge to make predictions and decisions.
2. Unsupervised learning
Unlike supervised learning, unsupervised learning does not require labeled data and uses various clustering methods to detect patterns in large amounts of unlabeled data.
3. Reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning involves training an agent to act in a specific context by rewarding or punishing it for its actions.
4. Transfer learning
Transfer learning includes using knowledge from previous activities to learn new skills efficiently.
Now, for more understanding, let’s explore some machine learning examples.
Machine Learning Examples
Let’s understand machine learning more clearly through real life examples.
1. Image Recognition: Machine learning is applied to photos and videos to recognize objects, people, landmarks, and other visual elements. Google Photos uses ML to understand faces, locations, and other elements in images so they can be conveniently searched and categorized.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP allows machines to interpret language as humans do. Automated customer service chatbots, for example, use ML algorithms to reliably answer queries by understanding text and recognizing the purpose behind it.
3. Speech Recognition: ML is used to allow computers to understand speech patterns. This technology is used for voice recognition applications such as Amazon’s Alexa or Apple’s Siri.
4. Recommendation Engines: Machine learning algorithms identify patterns in data and make suggestions based on those patterns. Netflix, for example, applies machine learning algorithms to suggest movies or TV shows to viewers.
5. Self-driving cars: Machine learning is at the heart of self-driving cars. It is used for object detection and navigation, allowing cars to identify and navigate around obstacles in their environment.
Now, we hope you get a clear understanding of machine learning. Now is the perfect time to explore Artificial Intelligence (AI). So, without further ado, let’s dive into the AI.
Understanding artificial intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a type of technology that attempts to replicate the capabilities of human intelligence, such as problem solving, decision making, and pattern recognition. In anticipation of changing circumstances and new insights, AI systems are designed to learn, reason, and self-correct.
Algorithms in AI systems use data sets to obtain information, solve problems, and develop decision-making strategies. This information can come from a wide range of sources, including sensors, cameras, and user feedback.
Algorithms in AI systems use data sets to obtain information, solve problems, and develop decision-making strategies. This information can come from a wide range of sources, including sensors, cameras, and user feedback.
AI has been around for several decades and has grown in sophistication over time. It is used in various industries including banking, healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and even entertainment. AI is rapidly transforming the way businesses operate and interact with customers, making it an indispensable tool for many companies.
In the modern world, AI has become more common than ever. Businesses are turning to AI-powered technologies such as facial recognition, natural language processing (NLP), virtual assistants, and autonomous vehicles to automate processes and reduce costs.
Ultimately, AI has the potential to revolutionize many aspects of everyday life by providing people with more efficient and effective solutions. As AI continues to evolve, it promises to be an invaluable tool for companies looking to increase their competitive advantage.
We have many examples of AI associated with our daily lives. Let’s explore some of them:
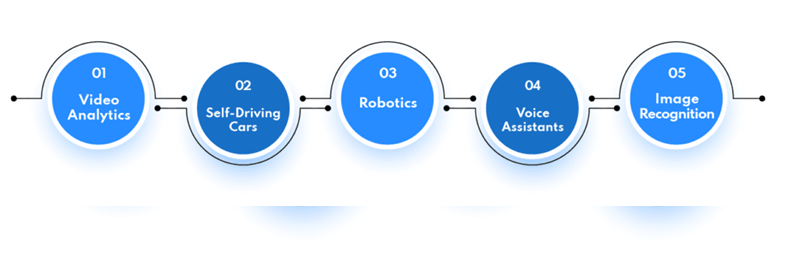
AI Examples
Some of the real life use cases of Artificial Intelligence are:
1. Video Analytics: Video Analytics is an AI application that analyzes video streams and extracts valuable data from them using computer vision algorithms. It can be used to detect unusual behavior or recognize faces for security purposes.
This technology is widely used in airports and hotel check-ins to recognize passengers and guests respectively.
2. Autonomous Cars: Autonomous cars are becoming more common and are considered an important example of artificial intelligence. They use sensors, cameras, and machine learning algorithms to detect obstacles, plan routes, and change vehicle speed based on external factors.
3. Robotics: Another important implementation of AI is robotics. Robots can use machine learning algorithms to learn how to perform various tasks, such as assembling products or exploring dangerous environments. They can also be designed to react to voice or physical instructions.
They are used in shopping malls to help customers and in factories to help with daily operations. Furthermore, you can also hire AI developers to develop AI-powered robots for your businesses. Apart from these, AI-powered robots are also used in other industries such as the military, healthcare, tourism, and more.
4. Voice Assistants: Artificial intelligence is used by virtual voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Home to understand natural language commands and respond appropriately. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is used by these voice assistants to understand user commands and respond with pertinent information.
5. Image Recognition: Image recognition is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) application that uses neural networks as a way to recognize objects in an image or video frame. It can be used in real time to identify objects, emotions, and even gestures.
The AI and machine learning examples are quite similar and confusing. Both look similar at first glance, but in reality, they are different.
In fact, machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence. To explain this more clearly, we will differentiate between AI and machine learning.
Machine Learning s Artificial Intelligence: the key differences!
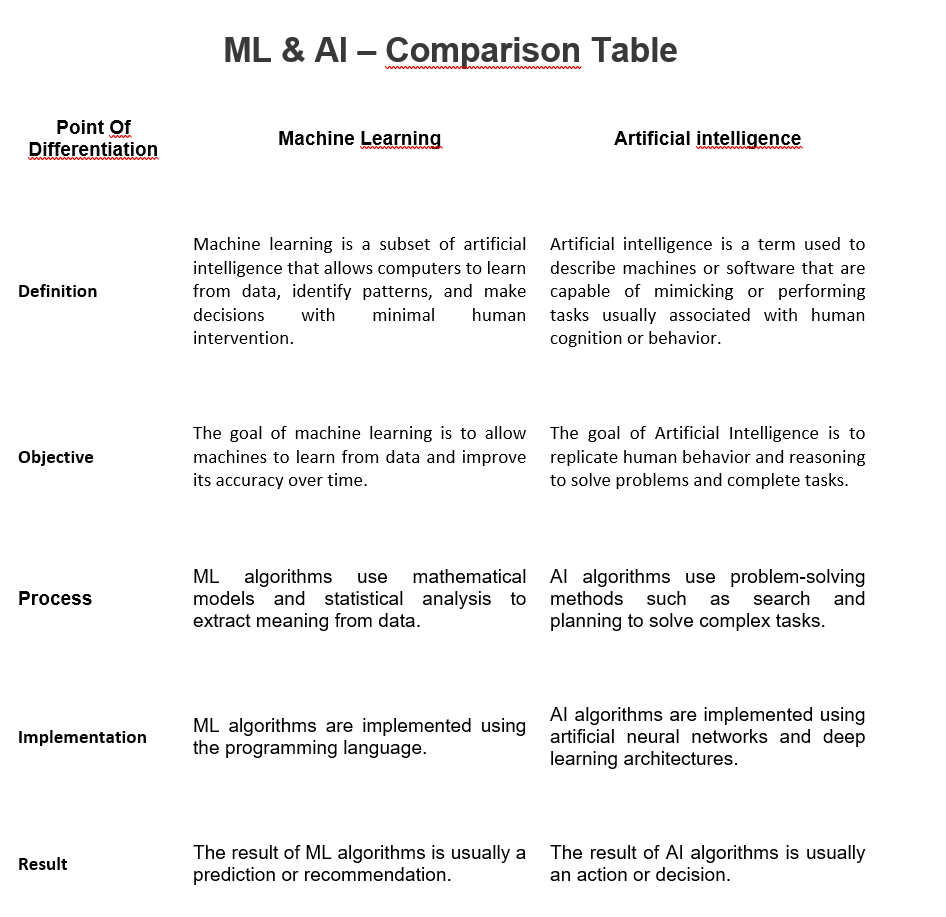
Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) are two related but different concepts. While both can be used to build powerful computing solutions, they have some important differences.
1. Approach:
One of the main differences between ML and AI is their approach. Machine learning focuses on developing systems that can learn from data and make predictions about future outcomes. This requires algorithms that can process large amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate insights from them.
AI, on the other hand, involves creating systems that can think, reason, and make decisions on their own. In this sense, AI systems have the ability to “think” beyond the data they are given and propose solutions that are more creative and efficient than those derived from ML models.
2. Type of problems they solve:
Another difference between ML and AI is the types of problems they solve. ML models are typically used to solve predictive problems, such as predicting stock prices or detecting fraud.
However, AI can be used to solve more complex problems such as natural language processing and computer vision tasks.
3. Computing power consumption:
Finally, ML models tend to require less computing power than AI algorithms. This makes ML models more suitable for applications where power consumption is important, such as mobile devices or IoT devices.
In simple words, machine learning and artificial intelligence are related but different fields. Both AI and ML can be used to create powerful computing solutions, but they have different approaches and types of problems they solve and require different levels of computing power.
Conclusion
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are two different concepts that have different strengths and weaknesses. ML focuses on developing algorithms and models to automate data-driven decisions.
On the other hand, AI emphasizes the development of self-learning machines that can interact with the environment to identify patterns, solve problems, and make decisions.
Both are important to businesses, and it’s important to understand the differences between the two to take advantage of their potential benefits. Therefore, it is the right time to get in touch with an AI application development company, equip your business with AI and machine learning and enjoy the benefits of these technologies.

