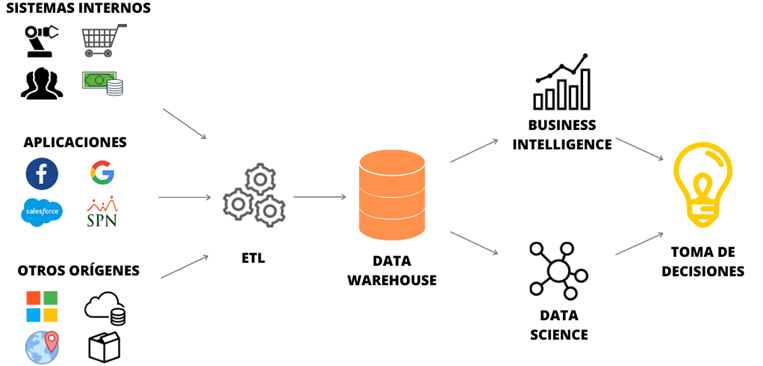
THE ABC OF DATA MANAGEMENT
1. Data integration
Organizations often have data scattered across multiple systems. Data integration involves combining data from different sources to obtain a complete and coherent view.
2. Data modeling
Data models are simple diagrams of your systems and the data those systems contain. Data modeling makes it easier for teams to see how data flows through their business systems and processes.
Here are some examples of information that a data model could include:
-
- Product dates
- Partner information
- Client data
3. Data storage
Data warehousing is the practice of recording and preserving data for the future, this serves to collect data over time. Once classified neatly, it is possible to access the information you need immediately and easily. In business it is used to make queries that make it easier to find solutions, make decisions and create strategies.
One of its most important functions is to allow businesses to generate and collect contact bases, such as:
-
- Customer information to analyze their purchasing trends
- Sales reports
- Product and service descriptions
- Human resources structure
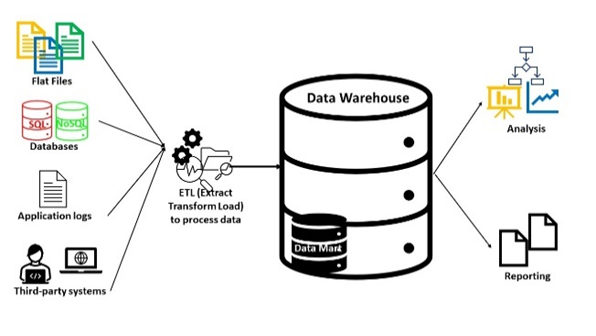
4. Data catalog
A data catalog is a detailed inventory of all of an organization’s data assets, designed to help data professionals quickly find the most appropriate data for any business or analytical purpose.
A data catalog uses metadata, data that describes or summarizes data, to create an informative and searchable inventory of all data assets in an organization. These assets may include:
-
- Structured data
- Unstructured data, including documents, web pages, email, social media content, mobile data, images, audio and video
- Reports and query results
- Data visualizations and dashboards
- Connections between databases
5. Data processing
Data processing refers to the set of actions and transformations performed on data to convert it from its original state into useful, meaningful and actionable information. This involves collecting, organizing, analyzing, manipulating, and presenting data in a way that allows people, systems, or applications to make informed decisions or perform specific tasks.
6. Data governance
Data governance, also known as data governance, is a set of practices, policies, procedures and processes used to manage and control data in an organization. The primary goal of data governance is to ensure that data is reliable, accurate, secure, and available to the right people and systems when needed. Data governance is essential to ensure data quality and to comply with data privacy regulations and standards.
7. Data Lifecycle Management (DLM)
DLM refers to a strategic and practical approach to managing data throughout its entire lifecycle, from its creation to its final deletion or archiving.
The data lifecycle comprises several stages, which can vary by organization and data type, but generally include:
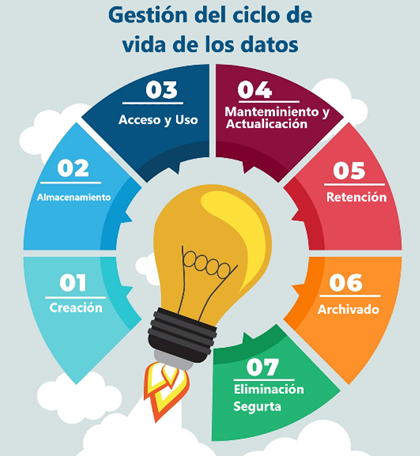
a. Creation: Data is initially created as a result of an activity or process, such as capturing customer information, generating transaction records, collecting sensor data, etc.
b. Storage: Data is stored in storage systems, whether on local servers, in the cloud, or on physical devices.
c. Access and Use: Data is used for various activities, such as analysis, reporting, decision making, real-time applications, among others.
d. Maintenance and Updating: The data may require periodic maintenance to ensure its accuracy and quality. This may include updating records, cleaning duplicate data, and correcting errors.
e. Retention: Data must be retained for a specific period to comply with legal regulations or business purposes. This may vary depending on the type of data and industry.
f. Archiving: After its retention period, data can be archived for long-term preservation, typically in lower-cost, slower-access storage systems.
g. Secure Deletion: When data is no longer needed, it should be securely deleted to protect the privacy and security of the information.
8. Data Pipeline (ETL)
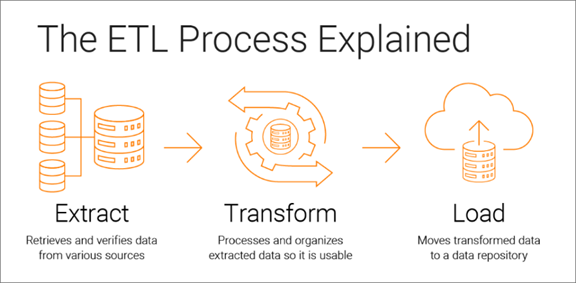
Data Pipeline (also known as data pipeline) is a set of processes and technologies that enable the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data from multiple data sources to a final destination, such as a database. data, a data warehouse or an analysis system. These pipelines are used to move data from one place to another efficiently and reliably, and are often a critical part of the data infrastructure in organizations.
Here is a description of the three main phases of a Data Pipeline:
-
- Extraction: In this phase, data is collected from various sources, which may include databases, file systems, cloud applications, web services, sensors, event logs, and more. Extraction involves obtaining raw data from these sources efficiently and generally involves the use of connectors and adapters specific to each data source.
-
- Transformation: After data is extracted, it often needs to be transformed and cleaned before it can be used for analysis or reporting. Data transformation can include format conversion, error correction, aggregation, normalization, and other processes to ensure data quality and consistency.
-
- Load: Once data has been extracted and transformed, it is loaded into a final destination, such as a database, data warehouse, or analytics system. Loading is done so that the data is available and ready for consultation and analysis by end users.
9. Data security
Data security, also known as cybersecurity or information security, refers to the practices, measures and technologies designed to protect an organization’s data and information from threats, attacks and unauthorized access. Data security is essential today due to the increasing amount of digital data stored and shared on computer systems and networks.
Aspectos importantes de la seguridad de los datos.
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
- Authentication and Authorization
- Encryption
- Vulnerability Management
- Monitoring and Detection of Threats

10. Data architecture
Data architecture refers to the structure and design of how an organization stores, organizes, processes and manages its data. It is an essential component of data management in a company or entity, and its main objective is to ensure that data is available, accessible, reliable and meets the business and technological requirements of the organization.